Multisource data fusion
Applied research
 Cliquez ici
pour obtenir la version française de ce document.
Cliquez ici
pour obtenir la version française de ce document.
Researchers
:
- Stanislas
de BÉTHUNE
-
Fabrice MULLER
In
the framework of applied research projects in digital cartography
and image processing, a new method of multiresolution image integration
was developed by the laboratory SURFACES.
An
important aim in the field of image integration techniques is to
produce color composites combining the information of high spatial
resolution satellite images with the multispectral information content
of much lower spatial resolution satellite images. Both the essential
spatial information of the high resolution image and the spectral
information content of the low resolution channels have to be preserved,
so as to produce pseudo high resolution spectral channels which
can be more easily interpreted or further processed for improved
classification or for other information extraction purposes.
The
methodology uses adaptive image filtering techniques, equalizing
the local mean and variance values of the high resolution image
to those of a lower resolution channel. The resulting high resolution
image still possesses its high structural information content while
having acquired at a local scale the spectral characteristics of
the low resolution channel.
In
order to merge a high spatial resolution image with three lower
resolution multispectral channels, these channels are first registered
to the high resolution image and resampled to the same pixel size.
The high resolution image is then merged separately with the three
channels, and the combination of the three resulting upgraded channels
allows to produce the desired color composite wich shows only minimal
distortion of the original multispectral values while being strongly
enriched in spatial information content.
High
resolution and low resolution satellite images are often separately
available for a given study area. The production of merged multiresolution
images provides the potentential customers with enhanced image data
allowing an improved interpretation analysis for map updating and
other spatial analysis applications.
Methodology
:
The multiresolution
merging of a high spatial resolution image with a low spatial resolution
channel tending to preserve the spectral characteristics of the low
resolution channel is performed in two steps :
First,
the low resolution channel is registered to the high resolution
image and resampled to the same pixel size (geometric correction). Next,
the high resolution image is adaptively filtered so that the local
means and variances measured within a moving window are adjusted
to the corresponding local means and variances of the low resolution
channel . This procedure tends to produce intensity matching of
the high resolution image to the actual intensity values of the
low resolution channel.
The
general Local Mean Variance Matching - LMVM - algorithm is used
to integrate two images, a high resolution image (H) into a low
resolution channel (L) resampled to the same size as H.
The
algorithm produces a simulated high spatial resolution image (F)
pertaining the spectral characteristics of the low resolution channel
(L). The small intensity differences between the merged image (F)
and the original low resolution channel corresponds to the structural
information content of the high resolution image. How well the spectral
values are preserved will depend on the size of the filtering window.
Small window sizes produce the least distortion. Larger filtering
windows incorporate more structural information from the high resolution
image, but with more distortion of the spectral values.
In
order to produce spatially enhanced color composites, the high spatial
resolution image is merged by the LMVM filter to the three selected
low resolution spectral channels separately. The resulting images
are then combined to produce the spatially enhanced color composite.
Results
:
This
methodology has been successfully applied for merging SPOT Panchromatic
(10 m) with SPOT XS (20 m) data, KOSMOS KVR 1000 (5 m) with SPOT
XS (20 m) data and, more recently, for merging IRS-1C Panchromatic
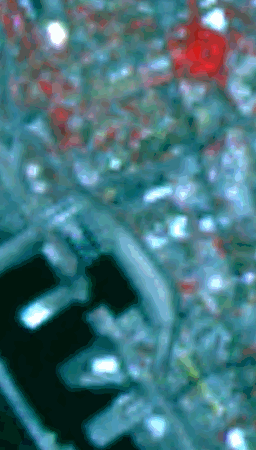
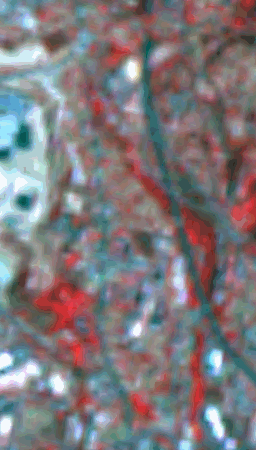
(5 m) and Multispectral (25 m ) images.
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1a. IRS-1C Panchromatic. |
Figure 1b. IRS-1C Multispectral. |
Figure 1c. Merged image. |
|
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 2a. IRS-1C Panchromatic. |
Figure 2b. IRS-1C Multispectral. |
Figure 2c. Merged image. |
BACK
|